By: Irfan Ahmed, expert in instant payments at BPC Banking Technologies
 In the global financial landscape, instant payments have experienced rapid growth, driving a true financial revolution with significant impacts on economic inclusion and citizen security. The speed, convenience, and security of instant payments have influenced the adoption of this model, so much so that by the end of 2022, more than 70 countries had already implemented a real-time payment (RTP) system, a market that currently handles 195.923 billion transactions. It is expected that by the year 2030, this number will exceed 1.455.250 billion transactions, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.02% between 2024 and 2030.
In the global financial landscape, instant payments have experienced rapid growth, driving a true financial revolution with significant impacts on economic inclusion and citizen security. The speed, convenience, and security of instant payments have influenced the adoption of this model, so much so that by the end of 2022, more than 70 countries had already implemented a real-time payment (RTP) system, a market that currently handles 195.923 billion transactions. It is expected that by the year 2030, this number will exceed 1.455.250 billion transactions, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.02% between 2024 and 2030.
Among the key factors driving market growth are the increasing use of smartphones worldwide, the interest of governments in incentivizing digital transactions, and the demand for fast settlements and clearings in money transfers between consumers and merchants.
Challenges of instant payments in Latin America
Around the world, there are notable examples of the impact of instant payments, one of the most significant being in India, where the UPI scheme has taken real-time payments to an unprecedented level. With settlement times of just five seconds or even less, this system is challenging the dominance of traditional payment cards and rapidly gaining market share.
According to a recent study, Brazil stands out as the second country with the highest volume of real-time transactions. In 2022, it recorded an impressive total of 29.2 million transactions, accounting for 15% of the global total. It was only surpassed by India, which reached the figure of 89.5 million. Additionally, the South American giant ranked third in terms of fastest growth in the same period, with an astonishing year-on-year rate of 228.92%.
So what are the challenges faced by financial institutions and Fintech companies in the region to develop a successful model like the one in Brazil?
- Technological Infrastructure: In most Latin American countries, there is still a lack of technological infrastructure to offer real-time payment services, and building it requires funding and government commitment.
- Interoperability: Eliminating closed systems and promoting an inclusive and interoperable platform where all participants (banked or unbanked) can interact and exchange funds without restrictions under regulatory supervision.
- Security: Preventing fraud and ensuring transaction security is a challenge due to the speed of the system, which requires tools to perform identity checks before the transaction is completed.
Overcoming these challenges requires continuous collaboration between regulatory authorities, financial service providers, and consumers to ensure the sustainable and secure development of real-time payments in the region.
What are the key components of a next-generation instant payments system?
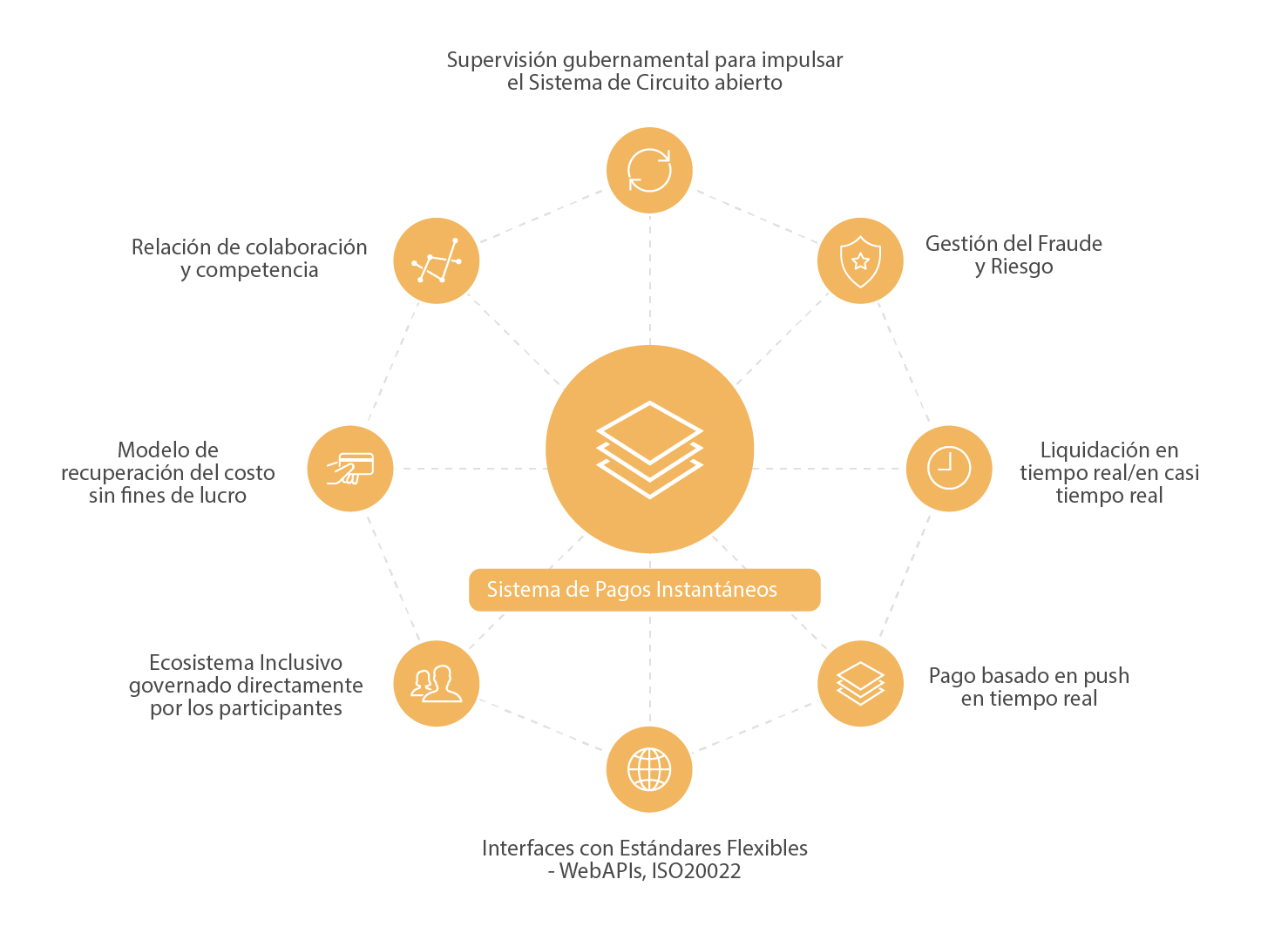
A next-generation instant payments system requires governmental oversight, real-time settlement and robust fraud management, among other elements:
- Governmental Oversight: Regulatory intervention is essential to guarantee true interoperability, enabling all payment agents, regardless of their size, to access the payment system and its use cases directly and without restrictions. This helps overcome entry barriers and fosters a fair and competitive environment in the sector.
- Collaboration and Competition: Striking an appropriate balance of collaboration and competition among participating institutions is crucial to create a truly competitive system. It is essential to maintain equal opportunities and growth possibilities for all actors in the ecosystem while avoiding market monopolies. Rules should prevent price wars in basic services, which should be either free or have a fixed cost. Competition can focus on new services and value-added services while ensuring that access to basic payment services is affordable for the general public.
- Cost Model: In countries where there are no charges for basic services like person-to-person transfers, the adoption of instant payments is considerably higher than in countries where charges exist. To encourage the adoption of digital payments, it is important to manage the payment scheme as a non-profit organization in the initial stages, especially in countries where consumers have not fully embraced digital payments yet.
- Inclusive and Participatory Ecosystem: Implementing a national instant payment system may face resistance from existing participants who wish to maintain the status quo. However, by allowing them to play a direct role in the governance and rules of the payment scheme, greater acceptance and adoption of digital payments can be promoted. Participation of financial institutions in defining rules and operational procedures generates a sense of ownership, leading to faster adoption of real-time payments and potentially driving new use cases and business opportunities for all market actors.
- Real-Time Push Payments: This is the most basic case of a real-time payment system, where funds are transferred from one account to another immediately. This mode ensures settlement in seconds and instant confirmation for both the beneficiary and the payer. Payments are irrevocable and do not require costly reversal processes, enabling the offering of low-cost or even free services to customers.
- Real-Time Settlement: It presents a challenge for participants such as Fintech companies, e-money providers, and microfinance institutes that do not have a funding account with a central bank for direct settlement and must use clearing agents (mainly banks). This method carries a risk of liquidity shortfalls, which can be mitigated in three ways: first, opting for settlement between participating institutions once funds transfer from the payer to the beneficiary; second, performing multiple settlement cycles during the business day, which may incur additional costs; and third, applying liquidity limits on debit transactions performed by participants.
- Fraud and Risk Management: Fraudsters take advantage of the openness of the payment system and the massive adoption of digital payments to attack users and steal funds. Having security systems that monitor and stop fraud in real-time is essential to protect users and instill confidence in the payment system. Early detection and immediate intervention are crucial to prevent financial losses and ensure transaction security.
About BPC
In the context of instant payments, time is essential. That’s why SmartVista Instant Payments was designed to integrate with virtually any infrastructure. The implementation is quick and offers a wide range of pre-configured options currently available to integrate with central banks, channels, and affiliate solutions, such as sanctions detection, commercial activity monitoring, and other solutions.
SmartVista offers an agnostic, versatile, and compatible solution with different instant payment structures that easily integrate with internal systems to provide additional capabilities such as message enrichment and liquidity management. It also allows the integration of real-time payments with a wide range of data sources through APIs.
The experience of having implemented instant payments worldwide represents an additional advantage, as experience is crucial when seeking a fast and efficient response.
About Irfan Ahmed
Irfan has over two decades of experience in the field of payment systems and digital financial solutions. He has been involved in the architectural design and project management of national payment switches, payment gateways, internet banking solutions, and mobile financial solutions. Irfan has provided domain-level consultancy to more than 40 banks worldwide in creating digital financial solutions throughout his career at BPC. He currently leads the Pre-sales division for the Middle East and Africa at BPC.

